js 实现拖动边框改变两个相邻 div 的宽度
2024-07-15 21:08:36
一、效果演示
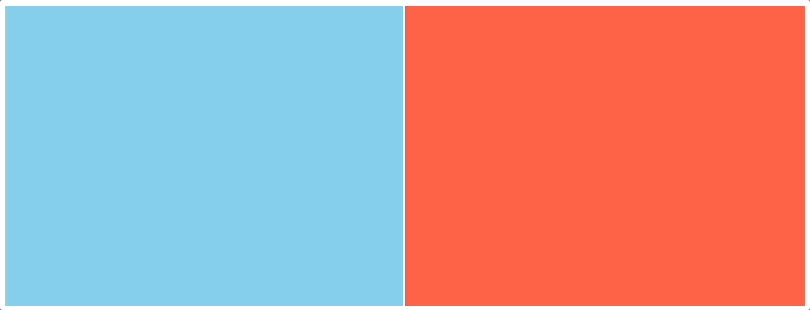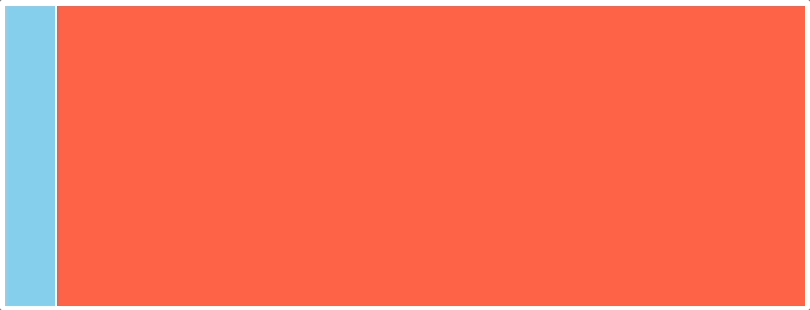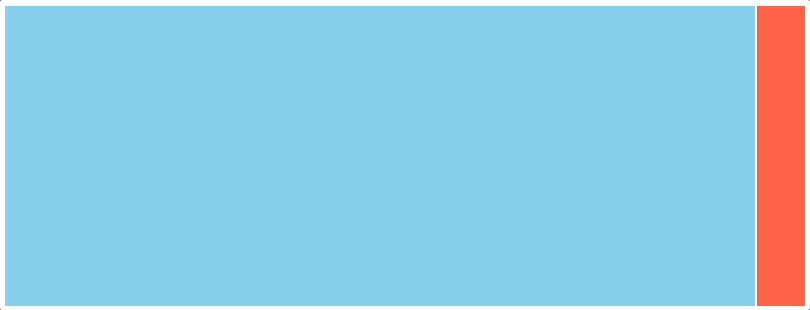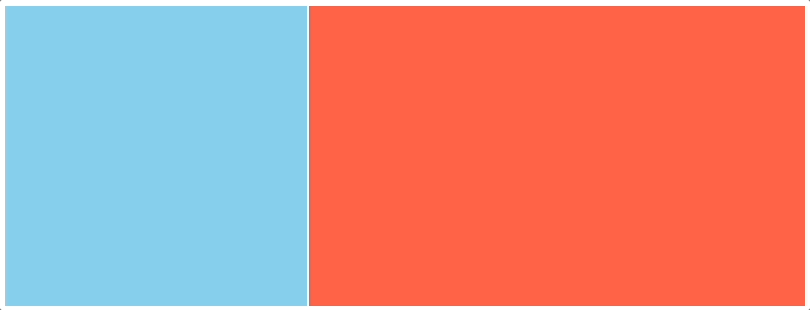
二、代码实现
完整代码如下。
<style>
.wrapper {
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
overflow: hidden;
margin-left: 200px;
/* 拖动条宽度 */
--bar-width: 2px;
.left {
width: calc(50% - var(--bar-width));
height: 100%;
background: skyblue;
float: left;
}
.bar {
width: var(--bar-width);
height: 100%;
cursor: col-resize;
float: left;
}
.right {
float: right;
width: 50%;
height: 100%;
background: tomato;
}
}
</style>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="bar"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
<script>
const wrapperEl = document.querySelector('.wrapper')
const barEl = document.querySelector('.bar')
const leftEl = document.querySelector('.left')
const rightEl = document.querySelector('.right')
barEl.onmousedown = function (e) {
// 容器 wrapper 左边距离浏览器左边的距离。见下图示意
const wrapperElOffsetLeft = wrapperEl.offsetLeft
// 拖动条 bar 上鼠标点击位置距离拖动条左边的距离。见下图示意
const barElOffsetX = e.offsetX
document.onmousemove = (e) => {
// 外部容器宽度
const wrapperWidth = wrapperEl.offsetWidth
// 拖动条宽度
const barWidth = barEl.offsetWidth
// 拖动条 bar 左边坐标 = 当前鼠标位置 clientX - 容器 wrapper 左边距离浏览器左边的距离 - 拖动条 bar 上鼠标点击位置距离拖动条左边的距离
const barLeft = e.clientX - wrapperElOffsetLeft - barElOffsetX
// 限制拖动最小宽度
if (barLeft < 50 || barLeft > (wrapperWidth - 50)) {
return
}
// 通过 js 改变元素样式
barEl.style.left = barLeft + 'px'
leftEl.style.width = barLeft + 'px'
rightEl.style.width = (wrapperWidth - barLeft - barWidth) + 'px'
}
document.onmouseup = (e) => {
document.onmousemove = null
document.onmouseup = null
}
}
</script>
原理: 拖动条 (.bar) 相对于父元素 (.wrapper) 是 absolute 定位,鼠标拖拽拖动条时,要实时计算出拖动条相对于父元素的 left 值,从而改变左右两个 div 块的宽度。
(下图为了方便说明,把拖动条的宽度改的非常大,拖动条中间的小黑点就是鼠标点击的位置)

↶ 返回首页 ↶
本文总阅读量 次